Thyroid Surgery
The thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is a gland located in the neck that plays a crucial role in regulating body functions by producing thyroid hormones, which affect metabolism and the functions of various organs. Thyroid problems are categorized into either an overactive or underactive thyroid function.
Symptoms of an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism):
- Increased heart rate.
- Elevated body temperature and excessive sweating.
- Digestive disturbances like diarrhea.
- Tremors and shakiness.
- Psychological symptoms such as anxiety and nervousness.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Irritability and mood swings.
Symptoms of an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism):
- Decreased heart rate.
- Weight gain.
- Severe fatigue and tiredness.
- Dry skin and hair loss.
- Digestive issues like constipation.
- Slowed movements and sluggish thinking.
- Decreased mood and depression.
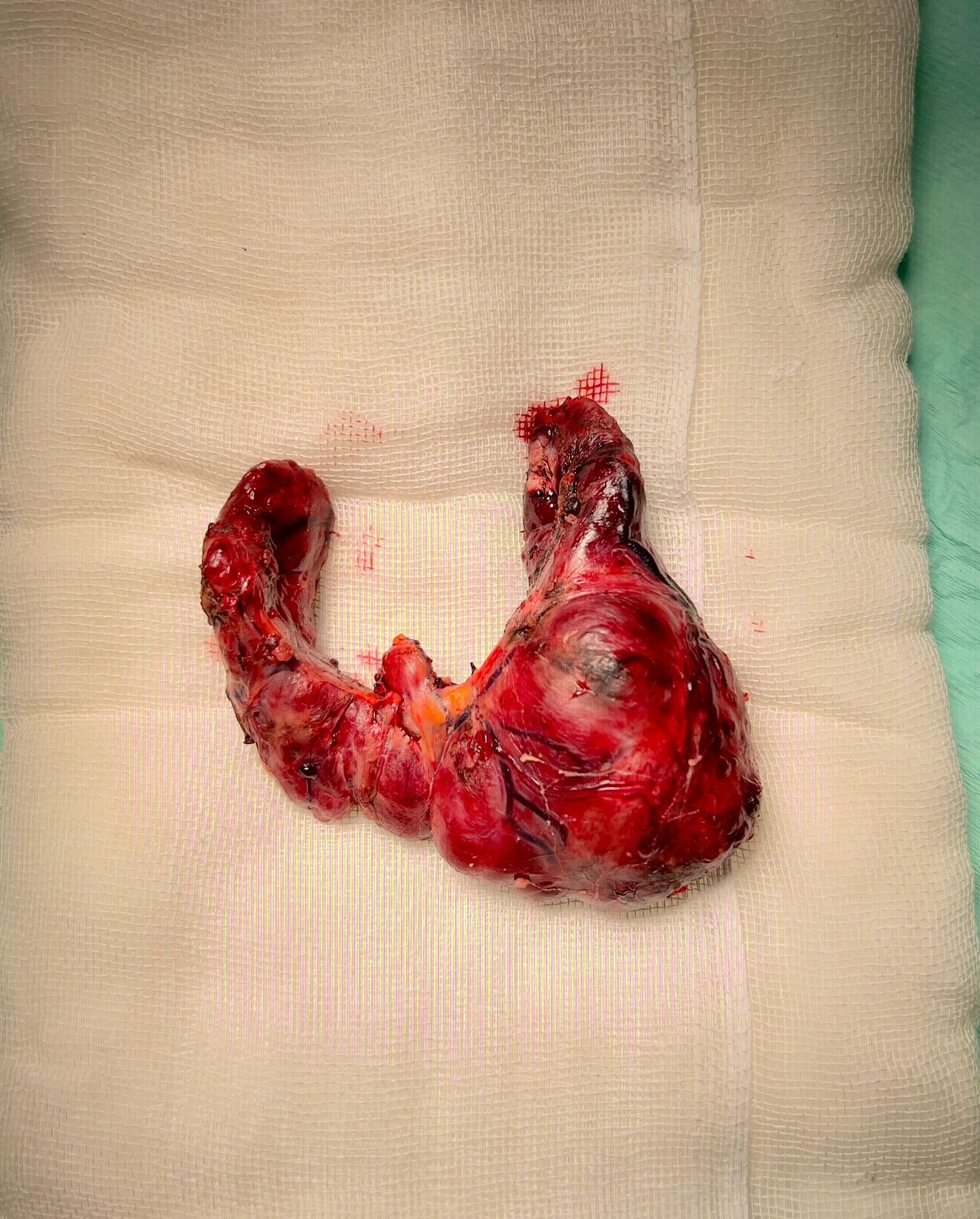
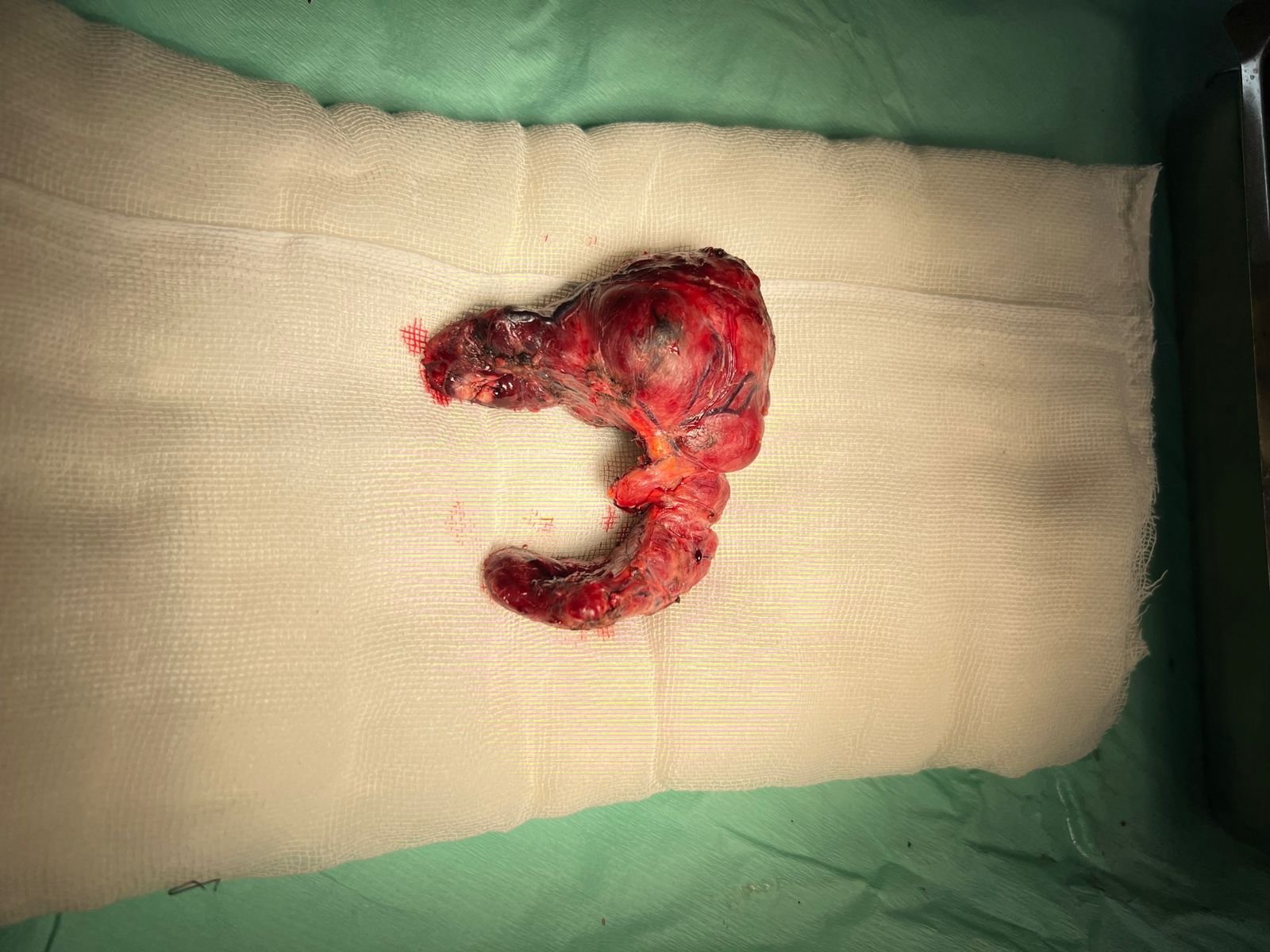
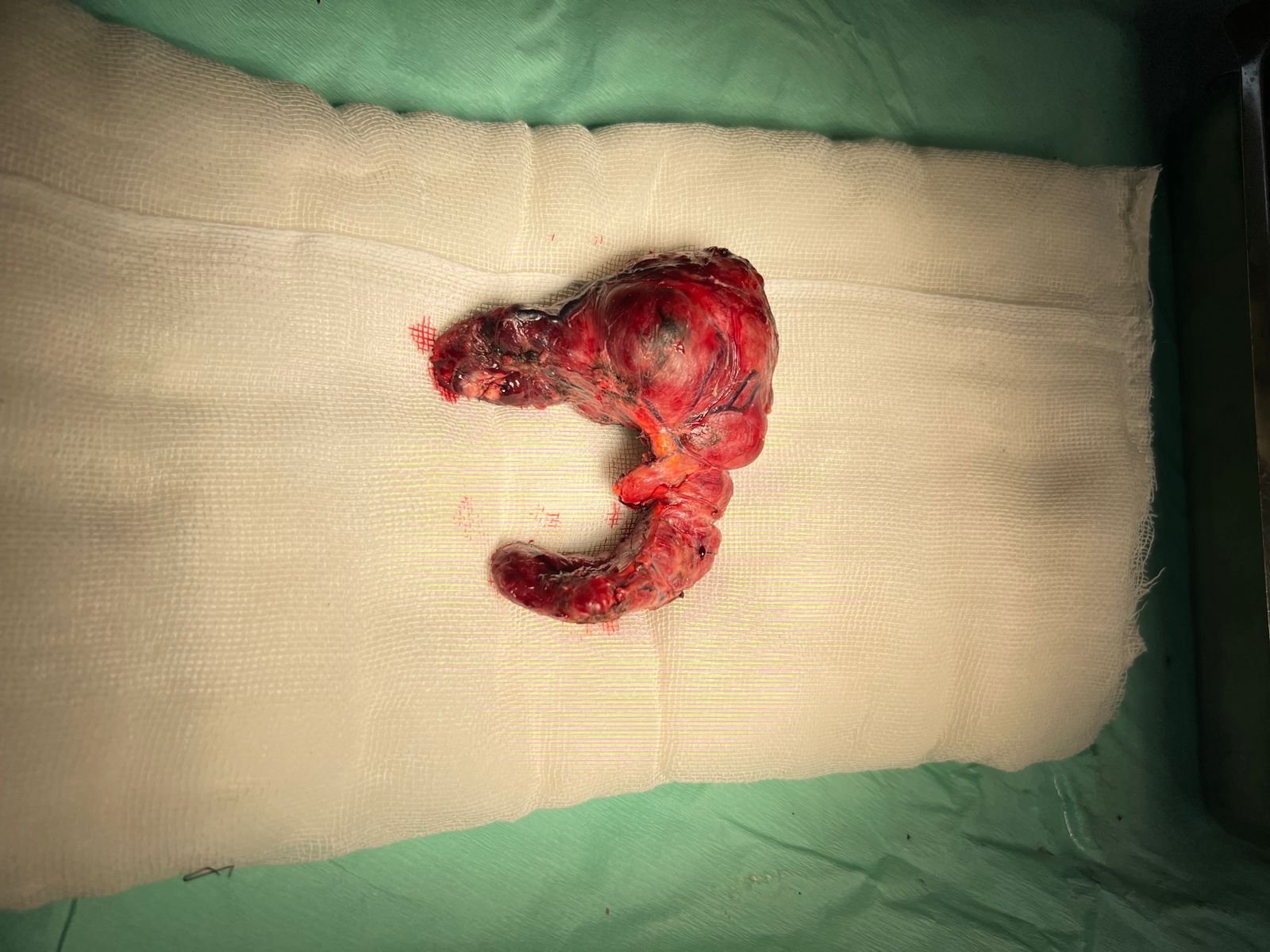
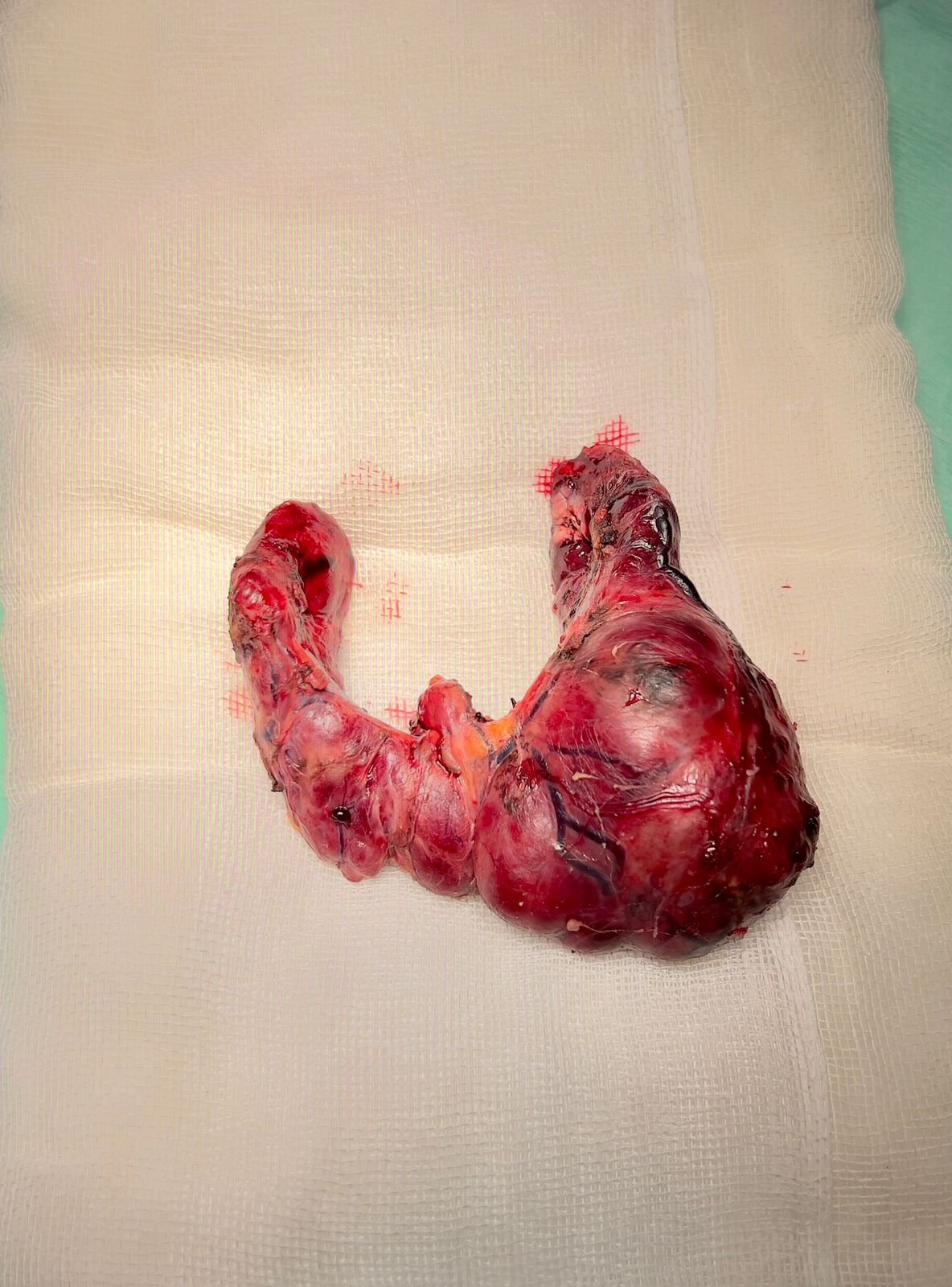
Surgical treatment for thyroid conditions is necessary under specific circumstances when other treatments, such as medications or radioactive iodine therapy, have not been effective or when there are indications of potential malignancy (cancer). The surgical procedure is known as a thyroidectomy, which involves the removal of all or part of the thyroid gland.
Surgical intervention is essential in the following cases:
- Thyroid Cancer
- Large Goiters
- Hyperthyroidism Unresponsive to Other Treatments
- Suspicion of Malignancy
- Recurrent Thyroid Conditions